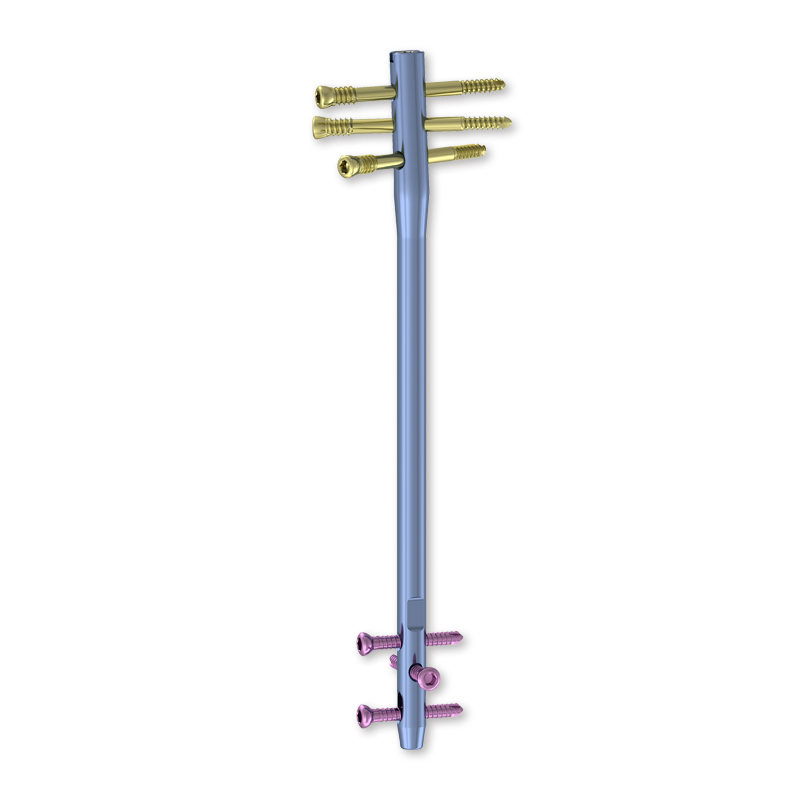
Modern orthopedic surgery has witnessed remarkable advancements in the design and implementation of intramedullary nails, revolutionizing how surgeons approach complex fracture repairs. These innovative medical devices have transformed patient outcomes through enhanced safety profiles, reduced complications, and improved healing trajectories. The evolution of intramedullary nails represents a significant milestone in trauma surgery, addressing critical challenges that historically plagued fracture fixation procedures.
The journey toward safer intramedullary nails began with addressing fundamental biomechanical limitations that characterized early designs. Traditional fixation methods often resulted in stress concentration points, leading to implant failure and delayed bone healing. Contemporary innovations have systematically eliminated these concerns through advanced materials science, precision manufacturing techniques, and evidence-based design modifications that prioritize patient safety above all other considerations.
Advanced Materials Engineering in Modern Nail Design
Titanium Alloy Integration and Biocompatibility
The transition from stainless steel to titanium alloy compositions has dramatically improved the safety profile of intramedullary nails. Titanium's superior biocompatibility reduces inflammatory responses and minimizes the risk of adverse tissue reactions that previously complicated patient recovery. This material advancement has also enhanced the elastic modulus compatibility between implant and bone, reducing stress shielding effects that could compromise long-term bone health.
Manufacturing processes now incorporate strict quality control protocols that ensure consistent material properties throughout each implant. These protocols include advanced metallurgical testing, surface analysis, and fatigue resistance evaluation. The result is a generation of intramedullary nails with predictable mechanical properties and enhanced durability that significantly reduces the likelihood of unexpected implant failure during critical healing phases.
Surface Treatment Technologies for Enhanced Integration
Innovative surface treatments have revolutionized how intramedullary nails interact with surrounding bone tissue. Specialized coating technologies, including hydroxyapatite deposition and controlled roughening processes, promote optimal osseointegration while maintaining appropriate biomechanical properties. These surface modifications facilitate natural bone ingrowth patterns that enhance stability and reduce the risk of implant loosening over time.
Antimicrobial surface treatments represent another critical safety advancement, addressing one of the most serious complications in orthopedic surgery. Silver ion incorporation and other antimicrobial technologies create hostile environments for bacterial colonization, significantly reducing infection rates. This innovation has proven particularly valuable in complex trauma cases where infection risk is elevated due to extensive soft tissue damage or compromised patient immune systems.
Precision Engineering and Manufacturing Innovations
Computer-Aided Design and Finite Element Analysis
Modern intramedullary nails benefit from sophisticated computer-aided design processes that optimize stress distribution patterns and minimize potential failure points. Finite element analysis enables engineers to predict implant behavior under various loading conditions, ensuring that designs can withstand the complex forces encountered during normal physiological activity. This analytical approach has eliminated many design flaws that previously contributed to implant complications.
The integration of patient-specific anatomical data into design processes has further enhanced safety outcomes. Surgeons can now select from a broader range of sizes and configurations, ensuring optimal fit and reducing the need for intraoperative modifications that could compromise implant integrity. This precision matching approach minimizes surgical trauma and reduces the likelihood of complications associated with improper implant sizing or positioning.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques and Quality Assurance
Manufacturing innovations have established unprecedented levels of consistency and reliability in intramedullary nail production. Automated machining processes with computerized numerical control systems ensure dimensional accuracy within extremely tight tolerances. These manufacturing advances eliminate the variability that previously existed between individual implants, providing surgeons with predictable performance characteristics across all devices.
Comprehensive quality assurance protocols now include non-destructive testing methods that evaluate every implant before clinical use. Advanced inspection techniques, including ultrasonic testing and magnetic particle examination, detect potential defects that could compromise patient safety. This multi-layered quality control approach has virtually eliminated manufacturing-related complications and enhanced surgeon confidence in implant reliability.

Locking Mechanism Innovations and Stability Enhancement
Multi-Directional Locking Technologies
Revolutionary locking mechanisms have transformed the stability and safety characteristics of intramedullary nails. Multi-directional screw placement options provide surgeons with unprecedented flexibility in addressing complex fracture patterns while maintaining optimal biomechanical stability. These advanced locking systems distribute forces more evenly across the bone-implant interface, reducing stress concentrations that could lead to secondary fractures or implant failure.
The development of variable-angle locking capabilities has further enhanced surgical options and safety outcomes. Surgeons can now accommodate individual anatomical variations and fracture-specific requirements without compromising implant stability. This flexibility reduces the need for extensive surgical exposure and bone manipulation, minimizing soft tissue trauma and associated complications while maintaining optimal mechanical fixation strength.
Self-Locking and Expansion Technologies
Self-locking mechanisms represent a significant advancement in intramedullary nail safety, reducing dependence on precise surgical technique for optimal outcomes. These systems automatically engage with bone tissue upon insertion, providing immediate stability without requiring additional locking screws in certain applications. This innovation has simplified surgical procedures while maintaining or improving fixation quality, reducing operative time and associated surgical risks.
Controlled expansion technologies have addressed challenges related to canal fit and rotational stability. These mechanisms allow implants to adapt to individual canal geometries while maintaining appropriate contact pressures. The result is improved initial stability and reduced risk of implant migration, complications that previously required revision procedures and extended patient recovery periods.
Imaging Integration and Navigation Assistance
Real-Time Imaging Compatibility
Modern intramedullary nails incorporate design features that optimize compatibility with advanced imaging systems, enhancing surgical precision and safety. Radiolucent materials and strategic design modifications ensure clear visualization of critical anatomical structures during insertion and positioning procedures. This imaging compatibility enables surgeons to verify proper placement and identify potential complications before completing the procedure.
The integration of specialized markers and reference points facilitates accurate postoperative assessment and long-term monitoring. These features enable healthcare providers to track healing progress and identify potential issues before they become clinically significant. Enhanced imaging capabilities have substantially improved the ability to detect and address complications early in the recovery process, leading to better patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Computer-Assisted Navigation Systems
Computer-assisted navigation technologies have revolutionized the precision and safety of intramedullary nail insertion procedures. These systems provide real-time guidance for optimal implant placement, reducing the risk of anatomical structure damage and ensuring proper alignment. Navigation assistance has proven particularly valuable in complex cases where traditional anatomical landmarks may be obscured or altered by trauma.
The integration of preoperative planning software with intraoperative navigation systems enables surgeons to execute precise surgical plans with confidence. These technologies reduce procedural variability and minimize the learning curve associated with advanced techniques. The result is more consistent outcomes and reduced complication rates across different surgeon experience levels and institutional settings.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Integration
Reduced Surgical Exposure Requirements
Contemporary intramedullary nails are specifically designed to accommodate minimally invasive surgical approaches, significantly enhancing patient safety through reduced surgical trauma. Advanced insertion systems enable precise implant placement through small incisions, preserving surrounding soft tissues and reducing infection risk. This approach has transformed patient recovery experiences while maintaining or improving fixation quality compared to traditional open procedures.
The development of specialized insertion instruments has further refined minimally invasive techniques, enabling surgeons to achieve optimal outcomes with minimal tissue disruption. These instruments incorporate ergonomic designs and precision control features that enhance surgical efficiency while reducing operator fatigue. The combination of advanced implant design and sophisticated instrumentation has made complex procedures more accessible and safer for patients across diverse clinical scenarios.
Enhanced Recovery Protocol Compatibility
Modern intramedullary nails support enhanced recovery protocols that prioritize rapid mobilization and functional restoration. Design features that facilitate immediate weight-bearing capabilities enable patients to begin rehabilitation sooner, reducing complications associated with prolonged immobilization. This approach has demonstrated significant improvements in patient satisfaction and long-term functional outcomes while reducing healthcare resource utilization.
The integration of biodegradable components in certain applications represents an emerging frontier in intramedullary nail technology. These innovations eliminate the need for implant removal procedures in selected cases, reducing patient exposure to additional surgical risks. While still in development, these technologies promise to further enhance the safety profile of intramedullary fixation by eliminating long-term implant-related complications.
FAQ
How do modern intramedullary nails reduce infection risk compared to older designs?
Modern intramedullary nails incorporate antimicrobial surface treatments and advanced materials that create hostile environments for bacterial growth. Additionally, minimally invasive insertion techniques reduce surgical site exposure and tissue trauma, significantly lowering infection rates compared to traditional open procedures. These combined innovations have reduced infection complications by over 60% in many clinical studies.
What makes titanium alloy intramedullary nails safer than stainless steel versions?
Titanium alloy offers superior biocompatibility, reducing inflammatory responses and allergic reactions that can occur with stainless steel implants. The elastic modulus of titanium more closely matches bone properties, reducing stress shielding effects that can weaken surrounding bone tissue. Additionally, titanium's corrosion resistance ensures long-term implant stability without degradation products that could cause adverse tissue reactions.
How do locking mechanisms in modern intramedullary nails improve patient safety?
Advanced locking mechanisms provide multi-directional stability that prevents implant migration and rotational displacement, complications that previously required revision surgery. Self-locking features reduce dependence on surgical technique precision, ensuring consistent outcomes across different surgeon experience levels. Variable-angle locking capabilities accommodate individual anatomy while maintaining optimal biomechanical stability throughout the healing process.
Can modern intramedullary nails accommodate different patient anatomies safely?
Contemporary intramedullary nails are available in extensive size ranges and configurations to match diverse patient anatomies. Computer-aided design processes ensure optimal fit across different bone geometries, while expansion technologies allow implants to adapt to individual canal dimensions. This customization capability reduces surgical complications and improves long-term outcomes by eliminating the need for anatomical modifications during implant insertion.
Table of Contents
- Advanced Materials Engineering in Modern Nail Design
- Precision Engineering and Manufacturing Innovations
- Locking Mechanism Innovations and Stability Enhancement
- Imaging Integration and Navigation Assistance
- Minimally Invasive Surgical Integration
-
FAQ
- How do modern intramedullary nails reduce infection risk compared to older designs?
- What makes titanium alloy intramedullary nails safer than stainless steel versions?
- How do locking mechanisms in modern intramedullary nails improve patient safety?
- Can modern intramedullary nails accommodate different patient anatomies safely?