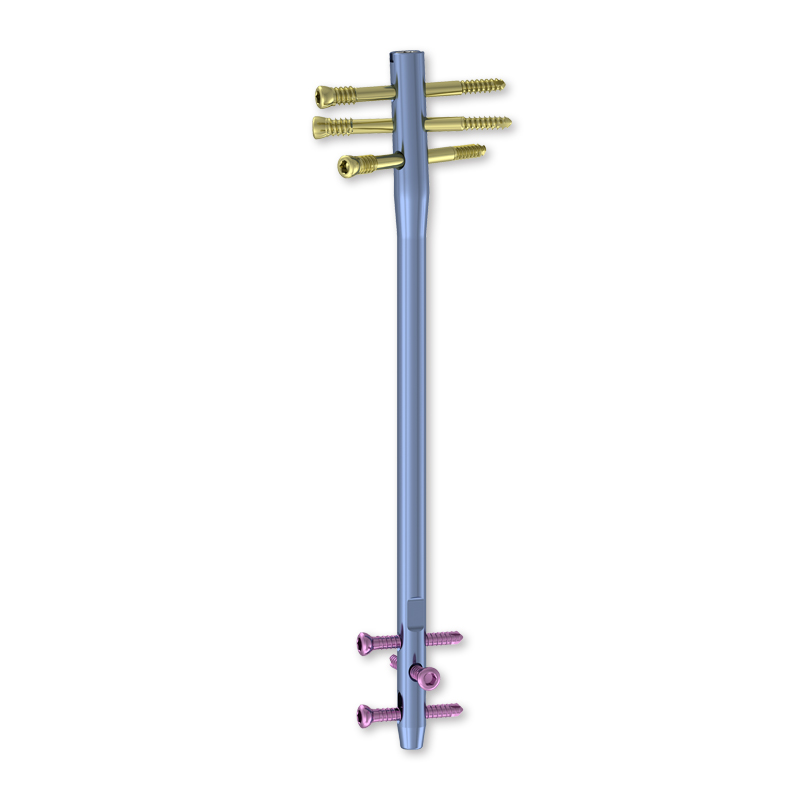
Long bone fractures represent some of the most challenging orthopedic injuries requiring precise surgical intervention to restore function and stability. Among the various surgical options available, interlocking nails have emerged as a revolutionary solution that addresses the complex mechanical demands of fracture healing while minimizing patient complications. These sophisticated devices combine the benefits of intramedullary fixation with enhanced rotational control, making them particularly effective for treating fractures in the femur, tibia, and other long bones. The success of this technique lies in its ability to provide immediate stability while allowing controlled micro-motion that promotes natural bone healing processes.
Biomechanical Advantages of Interlocking Nail Systems
Load Distribution and Stress Management
The biomechanical design of interlocking nails creates an optimal environment for fracture healing by distributing mechanical loads across multiple points of contact. Unlike traditional fixation methods that concentrate stress at specific locations, these devices spread forces along the entire length of the bone through the intramedullary canal. This distributed loading pattern reduces the risk of hardware failure while maintaining the bone's natural load-bearing capacity. The nail acts as an internal splint that shares mechanical stress with the healing bone, gradually transferring more load to the regenerating tissue as healing progresses.
Research demonstrates that properly positioned interlocking nails can withstand physiological loads that exceed normal daily activities, providing patients with confidence to begin early mobilization. The system's ability to handle both axial and rotational forces makes it superior to plates and external fixators in many clinical scenarios. Additionally, the nail's position within the medullary canal places it at the bone's neutral axis, where bending stresses are minimized, further enhancing the construct's durability and longevity.
Rotational Stability and Angular Control
One of the most significant advantages of interlocking nails is their superior rotational stability compared to simple intramedullary rods. The proximal and distal interlocking screws effectively prevent rotation around the nail's axis while maintaining the fracture's anatomical alignment. This rotational control is crucial for proper bone healing, as excessive motion at the fracture site can disrupt callus formation and lead to delayed union or nonunion. The precise placement of these screws creates a rigid construct that maintains reduction throughout the healing process.
The angular stability provided by interlocking screws also prevents telescoping and shortening of the bone, complications that were common with earlier nail designs. Modern systems allow surgeons to choose between static and dynamic locking options, providing flexibility to accommodate different fracture patterns and patient needs. Static locking provides maximum stability for complex fractures, while dynamic locking allows controlled compression that can stimulate healing in appropriate cases.

Clinical Applications and Fracture Pattern Suitability
Femoral Fracture Management
Femoral fractures represent the most common indication for interlocking nail systems, particularly in cases involving the diaphyseal and metaphyseal regions. The femur's large medullary canal accommodates sizeable nails that can handle the significant mechanical demands placed on the thighbone during weight-bearing activities. interlocking nails have proven especially effective in treating comminuted femoral shaft fractures, where traditional plating techniques might compromise soft tissue coverage or fail under physiological loads.
The versatility of femoral interlocking systems allows surgeons to address various fracture patterns, from simple transverse breaks to complex segmental injuries. Recent advances in nail design have expanded their use to include proximal and distal femoral fractures that were previously considered challenging for intramedullary fixation. The ability to achieve and maintain reduction through minimally invasive techniques has made these devices the gold standard for most femoral shaft fractures in adults.
Tibial Applications and Outcomes
Tibial shaft fractures present unique challenges due to the bone's subcutaneous location and limited soft tissue coverage, making interlocking nails an attractive treatment option. These devices minimize additional soft tissue trauma while providing stable fixation that supports early weight-bearing and functional recovery. The tibia's anatomy requires specialized nail designs that accommodate its triangular cross-section and varying canal diameter, leading to the development of anatomically contoured implants.
Clinical studies consistently demonstrate superior outcomes with interlocking nails compared to external fixation or plating for tibial shaft fractures. The technique's success in managing open fractures is particularly noteworthy, as it avoids extensive soft tissue dissection while providing stable internal fixation. The reduced infection rates and improved functional outcomes associated with this approach have made it the preferred method for most tibial diaphyseal injuries.
Surgical Technique and Precision Requirements
Preoperative Planning and Imaging
Successful interlocking nail surgery begins with comprehensive preoperative planning that includes detailed imaging analysis and implant selection. Advanced imaging techniques, including CT scans and three-dimensional reconstruction, help surgeons assess fracture patterns, bone quality, and canal dimensions to select the appropriate nail size and configuration. This planning phase is critical for determining entry point locations, nail length, and screw placement strategies that will optimize construct stability and promote healing.
Modern surgical planning software allows for virtual implant placement and biomechanical analysis before surgery, reducing operative time and improving accuracy. The ability to template nail positioning and predict potential complications has significantly enhanced surgical outcomes while minimizing revision rates. Surgeons can now anticipate technical challenges and prepare alternative strategies, leading to more predictable results and improved patient satisfaction.
Intraoperative Navigation and Accuracy
The precision required for successful interlocking screw placement has driven the development of advanced navigation systems and targeting devices. These technologies help surgeons achieve accurate screw positioning while minimizing radiation exposure and operative time. Computer-assisted navigation systems can guide both nail insertion and screw placement, ensuring optimal construct geometry and reducing the risk of technical complications.
Fluoroscopic guidance remains essential for real-time visualization during nail insertion and locking screw placement. The development of radiolucent targeting systems has improved visualization while maintaining the accuracy needed for precise screw positioning. These advances have made the technique more accessible to surgeons while standardizing outcomes across different experience levels and practice settings.
Healing Mechanisms and Bone Biology
Controlled Micro-Motion Benefits
The concept of controlled micro-motion represents one of the most important principles underlying the success of interlocking nails in fracture healing. Unlike rigid fixation methods that completely eliminate motion at the fracture site, these devices allow small amounts of controlled movement that stimulate callus formation and promote secondary bone healing. This micro-motion creates mechanical signals that enhance osteoblast activity and accelerate the natural healing process while preventing excessive motion that could disrupt early healing.
Research in bone biology has shown that complete rigid fixation can actually delay healing by eliminating the mechanical stimuli necessary for optimal bone formation. Interlocking nails provide an ideal balance between stability and mobility, creating an environment that supports both immediate stability and long-term healing. The ability to modify the construct's stiffness through dynamic locking options allows surgeons to fine-tune the mechanical environment based on fracture characteristics and patient factors.
Vascular Preservation and Soft Tissue Advantages
The minimally invasive nature of interlocking nail insertion preserves the fracture site's blood supply, which is crucial for optimal healing outcomes. Unlike open reduction techniques that require extensive soft tissue dissection, nail insertion through small incisions maintains the fracture hematoma and preserves periosteal blood supply. This biological advantage translates to faster healing times, reduced infection rates, and better functional outcomes for patients.
The preservation of soft tissue attachments and blood supply is particularly important in high-energy trauma cases where tissue viability may already be compromised. Interlocking nails allow for stable fixation without further compromising the local biology, supporting the body's natural healing mechanisms. The reduced surgical trauma also contributes to shorter hospital stays and faster return to functional activities, improving overall treatment efficiency and patient satisfaction.
Complications Management and Prevention Strategies
Hardware-Related Issues and Solutions
While interlocking nails are generally successful, understanding potential complications and their management is crucial for optimal patient care. Hardware failure, including nail breakage or screw loosening, can occur in cases of delayed union or excessive loading before healing is complete. Modern nail designs have addressed many of these issues through improved materials science and better understanding of biomechanical principles, but surgeons must still be prepared to manage these complications when they arise.
The development of fatigue-resistant materials and improved manufacturing processes has significantly reduced the incidence of hardware failure in contemporary practice. However, patient factors such as bone quality, activity level, and compliance with weight-bearing restrictions continue to influence complication rates. Early recognition of potential problems through regular follow-up and imaging allows for timely intervention before major complications develop.
Infection Prevention and Management
Infection remains one of the most serious potential complications of any orthopedic implant surgery, and interlocking nails are no exception. However, the minimally invasive nature of nail insertion significantly reduces infection risk compared to open reduction techniques. Proper surgical technique, including appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis and sterile technique, is essential for preventing both superficial and deep infections that could compromise treatment outcomes.
When infections do occur, the management approach depends on the timing and severity of the infection. Early superficial infections may respond to antibiotic therapy alone, while deep infections often require surgical debridement and possibly implant removal. The development of antibiotic-coated nails and improved understanding of biofilm formation has led to better prevention strategies and treatment outcomes for infected cases.
Future Developments and Technology Integration
Smart Implant Technology
The future of interlocking nails lies in the integration of smart technology that can monitor healing progress and provide real-time feedback on implant performance. Researchers are developing sensor-embedded nails that can measure load distribution, detect loosening, and monitor bone healing through wireless communication systems. These smart implants could revolutionize fracture management by providing objective data on healing progress and alerting clinicians to potential complications before they become clinically apparent.
Advanced materials science is also contributing to nail development through the creation of bioactive coatings and resorbable components that could eliminate the need for implant removal in some cases. These innovations aim to create implants that not only provide mechanical support during healing but actively promote bone regeneration through controlled drug delivery or growth factor release.
Personalized Medicine Applications
The trend toward personalized medicine is influencing interlocking nail design through the development of patient-specific implants created using advanced manufacturing techniques. Three-dimensional printing technology allows for the creation of custom nails that perfectly match individual patient anatomy, potentially improving fit and reducing complications. This personalized approach could be particularly beneficial for patients with unusual anatomy or revision cases where standard implants may not provide optimal fixation.
Advances in genetic testing and bone metabolism research are also contributing to more personalized treatment approaches. Understanding individual patient factors that influence bone healing could help surgeons select the most appropriate implant design and post-operative management protocols. This precision medicine approach promises to improve outcomes while reducing complications and healthcare costs.
FAQ
How long does it take for bones to heal with interlocking nails
Bone healing with interlocking nails typically takes 12 to 16 weeks for most patients, though this timeline can vary based on factors such as age, bone quality, fracture complexity, and patient compliance with treatment protocols. Younger patients and those with simple fracture patterns often heal faster, while older patients or those with comminuted fractures may require longer healing periods. Regular follow-up appointments and imaging studies help monitor healing progress and determine when full weight-bearing activities can be safely resumed.
Can interlocking nails be removed after healing is complete
Interlocking nails can be removed after complete fracture healing, though removal is not always necessary unless the patient experiences symptoms or complications related to the implant. The decision to remove the nail depends on factors such as patient age, activity level, implant-related symptoms, and surgeon preference. Younger patients who return to high-demand activities may benefit from nail removal to eliminate the risk of future hardware-related problems, while older or less active patients may choose to leave the implant in place permanently.
What are the weight-bearing restrictions with interlocking nails
Weight-bearing restrictions with interlocking nails vary depending on the fracture pattern, bone quality, and surgical technique used. Many patients can begin partial weight-bearing immediately after surgery, progressing to full weight-bearing as healing progresses and clinical evaluation permits. Simple fractures in healthy bone may allow early full weight-bearing, while comminuted or unstable fractures may require longer periods of protected weight-bearing. Your surgeon will provide specific guidelines based on your individual case and monitor your progress through regular examinations and imaging studies.
Are there any long-term effects of having interlocking nails
Most patients experience excellent long-term outcomes with interlocking nails, with minimal impact on daily activities or quality of life. Some patients may experience mild symptoms such as weather sensitivity or occasional discomfort at the implant site, but these issues rarely significantly impact function. The nail's position within the bone generally does not interfere with future medical procedures or imaging studies, though patients should inform healthcare providers about the implant when undergoing certain medical procedures or MRI examinations.